Agri-food in China: a market between dependence and diversification
Agri-food in China: a market between dependence and diversification
A strategic market at the heart of global food tensions
In 2024, China imported 188 billion euros worth of agricultural and agri-food products. This impressive figure reflects a structural reality: despite its desire to move towards self-sufficiency, China must rely on imports to feed its population of 1.4 billion. Rapid urbanization, rising living standards, diversification of dietary habits and pressure on domestic production reinforce this underlying trend.
China’s trade balance is largely in deficit, as the country turns massively to its partners to secure its supplies. 25% of its imports come from Brazil, the main supplier of soy and meat, 12% from the United States, and 8% from the European Union. Also noteworthy: the rise of Asian partners such as Thailand (6%), a sign of the regionalization of trade.
Agri-food in China: a growing sector, targeted needs
Among the agri-food products imported into China, 57% are raw agricultural products, notably :
- Oilseeds (30% alone),
- Meats (11%)
- Aquatic products (9%)
- Cereals (7%)
- Fats and oils (6%)
Processed products, including ready-made meals, preserves, sauces and cold meats, account for 45% of Chinese food imports. Finally, alcoholic beverages still account for a small share (2%), but they concentrate a high value and premium demand, particularly in the European wine segment.
This segmentation illustrates strong demand for plant and animal proteins, raw materials and processed products, in response to new consumer habits.
Rising food expenditure reflecting increased purchasing power
In 2024, the average annual food expenditure of Chinese households will reach 32,994 yuan, or around 4,300 euros. This already significant sum climbs sharply in the major metropolises: up to 7,300 euros in Shanghai and 6,786 euros in Beijing. This trend, linked to urbanization, the development of the middle classes and growing purchasing power, is stimulating demand for varied, safe, premium and practical products.
Chinese food imports on the rise
The Chinese market for imported food products is growing at an annual rate of 15%, well above the world average of 4%. Among imported products, the meat and charcuterie sector is experiencing strong growth, with 6.6 million tonnes in 2023, over +2.25% on the previous year[1] . Consumption of ready-to-eat products and snacks is booming, in line with the lifestyles of young urbanites, who prefer quick, healthy and even innovative solutions.[2]
This dynamism offers particularly interesting opportunities for companies capable of combining quality, innovation and understanding of the local market.
Europe as a leading partner for Chinese supplies
In 2024, China imported €14.5 billion worth of European agricultural and food products. This figure is rising, with France leading the way at 4.3 billion euros, followed by Spain, the Netherlands and Germany. What distinguishes Europe in this market is the complementarity of its national offerings: each country exports different products, which limits intra-European competition. Germany exports food preparations, Spain meat and pork products, France wines, cereals and dairy products, the Netherlands dairy products and cereal preparations.
France: European leader with rising exports
China imported 4.3 billion euros worth of French agricultural products in 2024, making France the leading European supplier to the Chinese market by value (30% of European imports are French). Between 2018 and 2023, its agri-food exports grew by 65%, a significant figure that underlines the potential of this commercial partnership.
China is now France’s 8th largest customer by value for agri-food products. France will be China’s 12th largest supplier in 2024.
French exports to China in 2024 are dominated by :
- Alcoholic beverages (37%), notably wines and spirits;
- Cereals (27%): France is the leading supplier of barley;
- Dairy products (9%), in constant growth.
These performances illustrate France’s ability to adapt to the expectations of Chinese consumers, particularly in terms of quality, safety and traceability.
Opportunities for international exporters in the agriculture and agrifood sector
The Chinese market offers numerous opportunities for foreign companies capable of offering :
- Traceable, safe products that comply with Chinese standards,
- Formats adapted to the local market and lifestyle,
- A premium or innovative image,
- Practical food solutions for the urban lifestyle.
Growth segments for all international players include :
- Upscale snacking,
- High added-value dairy products,
- Fruit, vegetables and processed products,
- Traditional cereals and breads adapted to local tastes.
Organic produce is also enjoying strong growth in China. By 2022, Chinese consumption of organic food products will be worth 12.4 billion euros, making China Asia’s leading market for organic products, and the 3rd largest in the world.
China’s growing export power in the agri-food sector
Alongside its imports, China is developing its own agri-food exports, which reached $95 billion in 2024. It is particularly active in :
- Seafood products (fish, shrimps),
- Processed fruit and vegetables,
- Cereals and cereal derivatives,
- Processed products such as sauces and preserves.
China is no longer content to import: it is becoming a global agri-food player, capable of competing in certain segments.
The Chinese agri-food market in full transformation
The Chinese agrifood market is undergoing rapid change, driven by sustained domestic growth, galloping urbanization and demanding consumers. For international players, it’s a promising but demanding market, requiring agility, consistency and a genuine local strategy. Importers must adapt by focusing on :
- Product innovation,
- Understanding local habits,
- Mastery of Chinese regulations,
- Building solid partnerships with local distributors and platforms.
For over 26 years, VVR International has been assisting food companies with their development projects in China. From strategic positioning, to developing brand awareness, to import and distribution procedures, VVR International’s experts support foreign companies every step of the way.
Sources:
Business France
[1] https://www.teamfrance-export.fr/fiche-marche/produits-alimentaires/viandes-et-charcuterie/CN
[2] https://www.lemoci.com/actualites/actualites/agroalimentaire-la-chine-continue-doffrir-des-opportunites-export-malgre-tout/


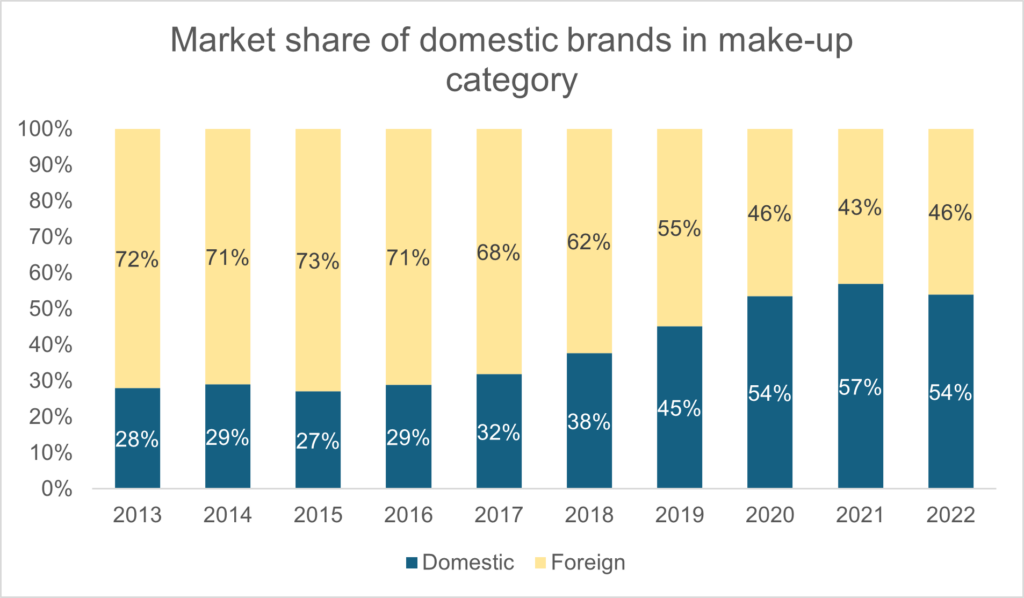 However, following strong growth between 2018 and 2022, with an average annual growth rate of almost 10.7%, the market is expected to fall slightly to around 7% per year over the next 5 years. This expansion is underpinned by several factors:
However, following strong growth between 2018 and 2022, with an average annual growth rate of almost 10.7%, the market is expected to fall slightly to around 7% per year over the next 5 years. This expansion is underpinned by several factors: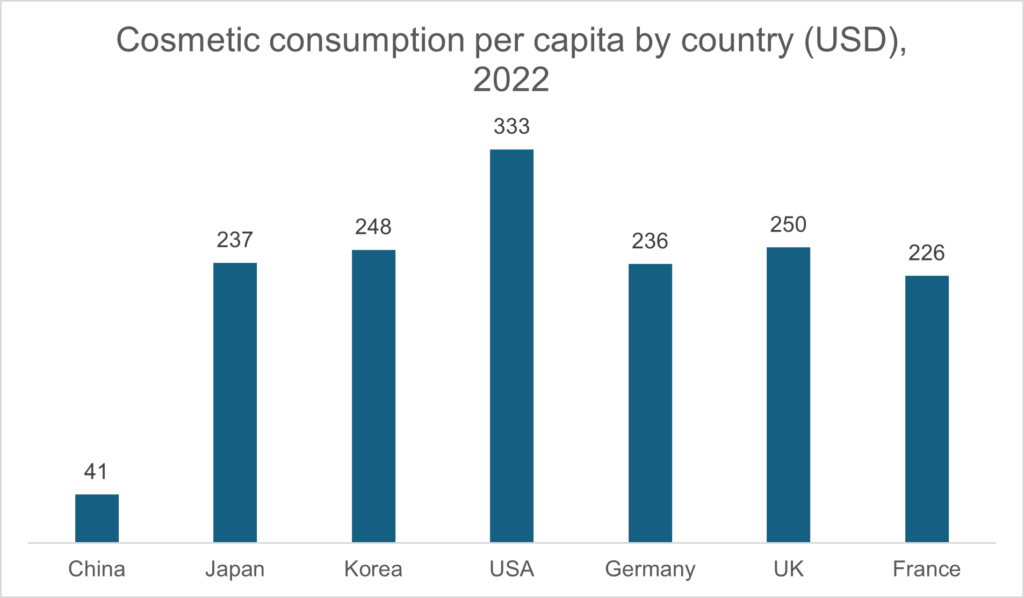 This rapid development is due to three main factors:
This rapid development is due to three main factors: