How to Make Your First Business Trip to China a Success | 2026 Guidance
Visiting China Factories: Your Ultimate Guide to Successful Business Trip to China
1. Introduction
China remains one of the most important global manufacturing hubs in 2025. For many companies, visiting Chinese factories is a crucial step toward securing reliable suppliers, auditing production quality, or negotiating partnerships. However, a business trip to China can feel overwhelming, especially for first-time travelers. Because different laws, cultural expectations, and logistical hurdles require careful preparation, planning ahead is essential.
For foreign companies, understanding how to navigate business trips in China is more than just logistics. It is about ensuring compliance with Chinese labor laws, managing cultural nuances, and protecting the well-being of staff. With the right preparation, companies can turn a factory visit into a long-term partnership opportunity. In this article, we, VVR RH, provide practical advice for business managers and HR leaders. It covers preparation, etiquette, travel tips, and HR recommendations for employers sending staff abroad. It also outlines common challenges and strategies to overcome them.
2. Key Takeaways
• Face-to-face meetings are essential in China’s business culture.
• A well-planned agenda ensures smooth visits to multiple factories.
• Compliance with visas, local labor laws, and cultural norms is vital.
• Understanding Chinese etiquette strengthens negotiations.
• Preparation reduces risks and increases trust with suppliers.
Insight for you: Many firms now follow a China+1 strategy, combining Chinese production with new bases in Vietnam, Malaysia, or Thailand. Business travel often covers China and one ASEAN partner, making it a cornerstone of modern supply chain planning
3. Before Your Business Trip to China: Preparation
Preparing thoroughly before your trip is crucial since China’s business culture values punctuality and planning. Therefore, the right documents, health checks, and digital readiness will help you avoid setbacks.
Plan Your Visit Agenda

Preparation and making an advanced plan are keys when entering China for your first business trip.
Travelling to China for business requires detailed preparation. Meetings should be scheduled 2–3 weeks in advance, as suppliers often need time to prepare documentation and sample production lines. You should be mindful of public holidays. During Golden Week (October) and Lunar New Year (January/February), many factories shut down for one to three weeks. Travel forums such as Reddit’s r/travelchina warn that last-minute planning around these periods often leads to delays.
Tip: Always check the official Chinese holiday calendar before confirming flights. Building flexibility into your agenda ensures fewer disruptions. Ensure agendas are realistic. Allow travel time between provinces because China’s geography is vast. Building flexibility into your agenda ensures fewer disruptions. Ensure agendas are realistic. Allow travel time between provinces because China’s geography is vast.
Business Trip to China: Visa Type (2025 Update)
China updated its business visa policy in 2024, simplifying procedures for short-term travelers while keeping compliance requirements for longer stays. The type of visa and the documents needed depend primarily on the duration and purpose of your visit.

Business travel to China requires an M visa type if you stay over 30 days.
Short-term Business Trips (Less than 30 days)
Until 30 January 2025, holders of ordinary passports from multiple countries, including France and Monaco, are exempt from visa requirements for visits of up to 30 days. This policy applies to trips for business, tourism, family visits, transit, or cultural exchanges. Travelers under this exemption can enter China without an M visa, provided their stay does not exceed 30 days, and they do not engage in activities that require residence or employment permits. Tip: Always carry a printed invitation letter or meeting confirmation from your Chinese partner. It may be requested by border officials upon entry.
Longer Business Stays (Over 30 days)
For business trips exceeding 30 days, business travelers typically require an M visa. Applicants must prepare the following:
- A formal invitation letter from a Chinese company or authorized institution.
- A valid passport (at least six months’ validity remaining).
- A completed visa application form and a recent passport photo.
Applications are typically submitted at the Chinese Embassy or Consulate in the applicant’s country of residence (for example, the Chinese Embassy in France). Fees depend on visa type, nationality, and processing speed. So, it’s advisable to apply well in advance. Frequent travelers can now apply for multi-entry M visas valid for six or twelve months. Standard processing takes 4–10 working days, with express options available. Moreover, most embassies now require fingerprints and biometric data during the application. Travelers also need an official invitation letter from the hosting company or local authority. Tip: Employers should bring a printed invitation letter from their Chinese partner to avoid bottlenecks when entering China. Delays in visa processing can disrupt entire factory visit schedules.
Health and Safety Updates
Beyond vaccination requirements, visitors must prepare for air quality challenges. In fact, Beijing, Xi’an, and other industrial cities frequently report high pollution levels. If you are a sensitive person, you should carry N95 masks. Companies are encouraged to provide corporate travel insurance covering medical emergencies, accidents, and even COVID-19 reinfections. Insurance should include emergency evacuation clauses, especially for employees visiting remote provinces.
Digital Preparation
China’s internet environment is highly regulated. Google, Gmail, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram are blocked. LinkedIn was restricted in 2023. Travelers should download Baidu Maps or Gaode Maps before arrival, as Google Maps does not function. Wi-Fi in airports and hotels often requires passport registration for access. Tip: Encourage employees to set up VPNs approved by the company. This ensures secure communication and uninterrupted access to critical apps.
4. Understanding Business Etiquette in China
Etiquette in China often determines whether business discussions succeed. In fact, respect, trust, and proper manners are as important as contracts. For example, greetings usually involve a handshake and a nod.
What Every Foreigner Should Know
Etiquette remains a central part of business in China. Meetings usually start with formal introductions and the exchange of business cards. Cards should be presented and received with both hands, followed by a brief review before storing them. Seating arrangements at banquets and meetings reflect hierarchy. Senior hosts sit in the middle. Foreign guests of honor sit opposite. Punctuality is highly respected. Arriving late, even by a few minutes, can be seen as disrespectful.
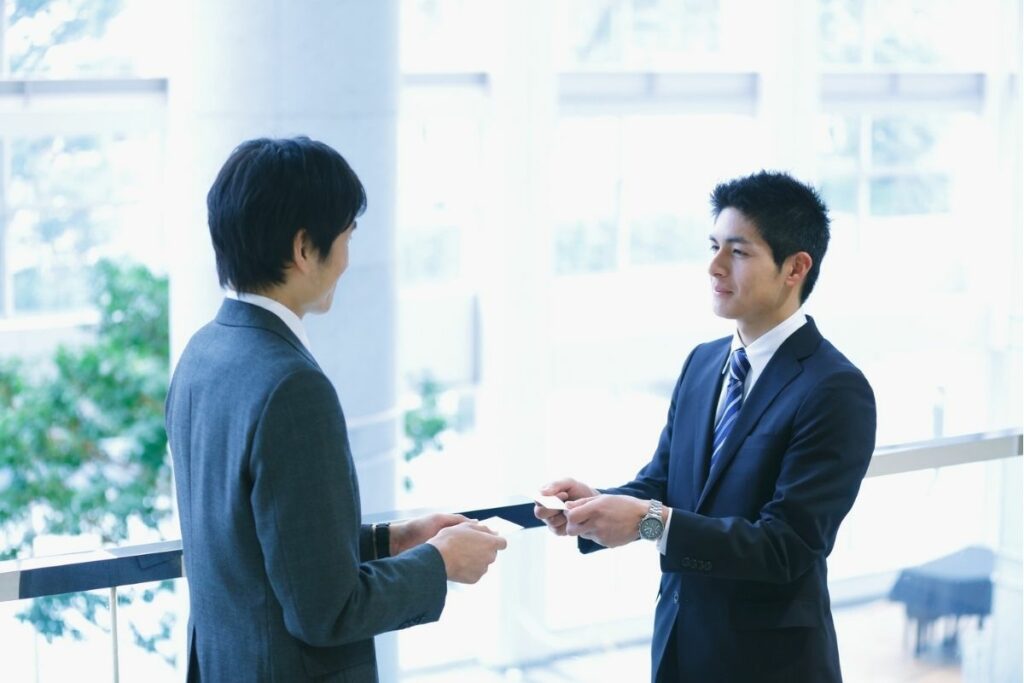

Business cards should be presented and received with both hands in China.
Communication Styles and Meeting Practices
Chinese managers often avoid saying “no” directly. Instead, phrases like “we will think about it” or “this might be difficult” suggest rejection. Reading between the lines is crucial. Important decisions are sometimes made outside the boardroom. Karaoke nights, banquets, and tea sessions are common venues for informal but essential discussions. Tip: Train your staff to interpret indirect communication styles. Misunderstandings in tone can derail negotiations.
Cultural Differences You Need to Adapt To
China is a collectivist society, based on Hofstede’s model. Group loyalty, harmony, and respect for hierarchy dominate the workplace. By contrast, Europe emphasizes individual decision-making. Consequently, decisions in China are made at the senior level, not by mid-level staff. Furthermore, uncertainty avoidance is moderate. While contracts are detailed, relationships (guanxi) often outweigh written terms. China also scores low on indulgence, meaning employees and partners often prioritize long-term stability over short-term rewards.
Building Long-Term Business Relationships
Trust in China grows slowly. Many factories prefer starting with small test orders before scaling up to larger deals. Consistency in follow-ups via WeChat is key. Sending a visit report and a polite thank-you note in Mandarin can make a lasting impression. HR Tip: Encourage employees to bring small branded gifts. These act as tokens of goodwill and reflect respect for local traditions.
5. Useful Tips During Trips to China
Once you arrive in China, practical knowledge makes the difference between a smooth trip and a stressful one. From payment apps to travel choices, preparation pays off.
Before You Board
China is vast, and weather conditions vary greatly. Guangzhou is hot and humid, while Harbin can be subarctic. Here are some tips for your first business trip to China.
- Clothing: Pack both formal business attire for meetings and casual wear for factory visits.
- Business cards: Always carry bilingual cards (English on one side, Mandarin on the other).
- Cash: Carry some RMB (Yuan), as smaller towns may not accept foreign cards.
- Apps: Download WeChat for communication and payments.
- Connectivity: Arrange an international SIM or eSIM for data.
- Power: Bring a portable charger; taxis and rural trains often lack charging ports.
On Arrival
Major airports such as Beijing Capital and Shanghai Pudong require fingerprint scans and face ID at immigration.
- Payment. Mobile payments dominate. WeChat Pay and Alipay now accept foreign Visa and MasterCard cards. Register accounts in advance to avoid problems. For currency exchange, ATMs often offer better rates than counters.
- Mobility. China’s high-speed rail system spans more than 42,000 km, the largest in the world. Popular routes like Beijing–Shanghai reduce travel to 4.5 hours. You should buy tickets in advance during peak travel. For smaller factory towns, hire a driver. If visiting factories in rural areas, you can arrange pickups with suppliers. Taxis rarely accept foreign cards and may refuse long-distance rides. Avoid unlicensed taxis. Besides, you can download and use DiDi (China’s Uber) for safe rides.
- Accommodation. Not all hotels can host foreigners. Always book international chain hotels or confirm foreigner-friendly status before arrival. Remember that confirmation before booking.
- Language. English is limited outside major cities. Hire interpreters for factory visits. Translation apps like iFlytek or Baidu Translate help but are not substitutes for human interpreters. HR Tip: Provide travelers with a pre-departure pack: emergency contacts, supplier addresses in Mandarin, and cash for small expenses.
After the China Business Trip & Following Up
The work does not end when you return home. Indeed, effective follow-up is critical in Chinese business culture. Chinese suppliers expect continued communication after an initial visit. For this reason, companies should send a visit report within two weeks, thank their hosts, and confirm next steps. Checklist for follow-up:
- Provide feedback on inspected goods.
- Clarify contracts, delivery terms, and compliance requirements.
- Maintain guanxi through regular WeChat
- Hold internal debriefs to evaluate whether travel goals were met.
HR Tip: Encourage employees to document cultural insights. This builds knowledge for future business trips and reduces risks for new travelers.
6. HR Recommendations for Employers Sending Staff to China
Employers should treat China business trips as part of broader HR planning. This ensures compliance, employee safety, and long-term business success. Longer trips (stays beyond 90 days) may require a Z visa (work visa) and a residence permit. Employers must also comply with China’s labor contract law if staff are assigned beyond short-term visits. Provide cultural training before departure. Employees should be prepared for long banquets, late-night negotiations, and formal etiquette.
Challenges to expect and how to overcome them
- Jet lag. China is 6–7 hours ahead of Europe and 12–13 hours ahead of the U.S. Encourage travelers to adjust schedules before departure.
- Cultural fatigue. Banquets often include heavy drinking. Offer staff polite ways to refuse alcohol if needed.
- Factory inspections. Some suppliers may showcase only their best production lines. Always conduct random checks.
- Connectivity. Internet restrictions may slow communication. Always carry offline maps and backup files.
Read more related articles
7. Conclusion
A business trip to China is not just a visit. It is an investment in long-term partnerships. Proper preparation ensures compliance, safety, and cultural alignment. For employers, supporting staff with training, insurance, and compliance checks turns a routine trip into a strategic advantage. Planning your first business visit to China? VVR International – VVR RH supports global companies with:
- HR outsourcing services.
- Recruiting and compliance with Chinese labor law.
- Cultural and travel preparation for staff.
- Employer of Record (EOR) solutions to test the market without heavy setup costs.
👉 Contact us today to transform your China business trip into long-term business growth.
FAQ
-
What are the main HR challenges in China that outsourcing helps foreign companies solve?
The main HR challenges in China include compliance with labor contract law, managing payroll across different cities, handling social insurance and housing fund contributions, and navigating work permit requirements for foreign employees.
HR outsourcing for foreign companies in China addresses these issues by providing local expertise, payroll outsourcing services, contract management under mutual agreement rules, and support for work permits. This allows companies to operate smoothly while minimizing legal and operational risks.
-
How do HR outsourcing services in China support strategic HR management and long-term growth?
HR outsourcing services in China support strategic HR management, aligning with modern HR practices in China, including digital HR solutions, employee retention strategies, and ESG-focused HR policies. By outsourcing HR functions, companies gain access to market insights, salary benchmarks, and compliance monitoring, enabling them to build sustainable teams in China while adapting to workforce trends and long-term business objectives.
Related Posts














 he seventh China Information Technology Expo took place between the 9 and the 11th of April 2019 in Shenzhen. In this event which gathered the World leaders of technologies, the visitors could discover and try the news and innovation like the Youxiaomei robot of the that served cups of tea. Although the exhibitors were from different nationalities, this event was a veritable vitrine for the Chinese progress in this sector.
he seventh China Information Technology Expo took place between the 9 and the 11th of April 2019 in Shenzhen. In this event which gathered the World leaders of technologies, the visitors could discover and try the news and innovation like the Youxiaomei robot of the that served cups of tea. Although the exhibitors were from different nationalities, this event was a veritable vitrine for the Chinese progress in this sector.